- +91 7012749886
- [email protected]
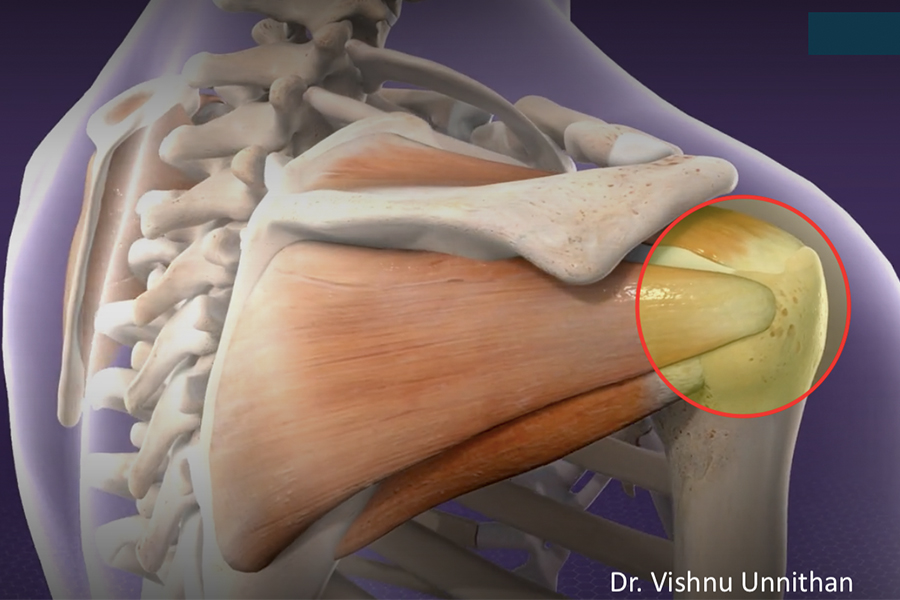
Tendinopathy is a term used to describe conditions related to the tendons, which are the thick cords that connect muscles to bones in the human body. Tendinopathy is a broad term that encompasses various tendon-related disorders and injuries, including calcific tendinopathy, tendonitis and tendinosis. These conditions can affect any tendon in the body, but they most commonly occur in the tendons of the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles.
It is a disorder in which calcium gets deposited in the tendon structures at its attachment areas near to the bone leading to severe inflammation and pain.
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a condition in which a tendon becomes inflamed. This inflammation is often a result of overuse, repetitive motions, or acute injuries. Tendonitis can cause pain, swelling, weakness and limited mobility in the affected area.
Tendinosis is a chronic condition in which the tendon degenerates over time. Unlike tendonitis, tendinosis does not typically involve significant inflammation. Instead, it involves the breakdown of collagen in the tendon. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and weakness.
Common causes and risk factors for tendinopathy include:
Treatment for tendinopathy typically involves rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Most cases requires stretches and strength training of the involved muscle groups. In some cases, more advanced treatments such as corticosteroid injections or, in severe cases, surgery may be necessary especially in cases like recalcitrant calcific tendinopathy.
It's important to address tendinopathy promptly to prevent the condition from worsening and potentially leading to long-term disability. If you suspect you have tendinopathy or are experiencing symptoms, it's advisable to get our opinion for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.