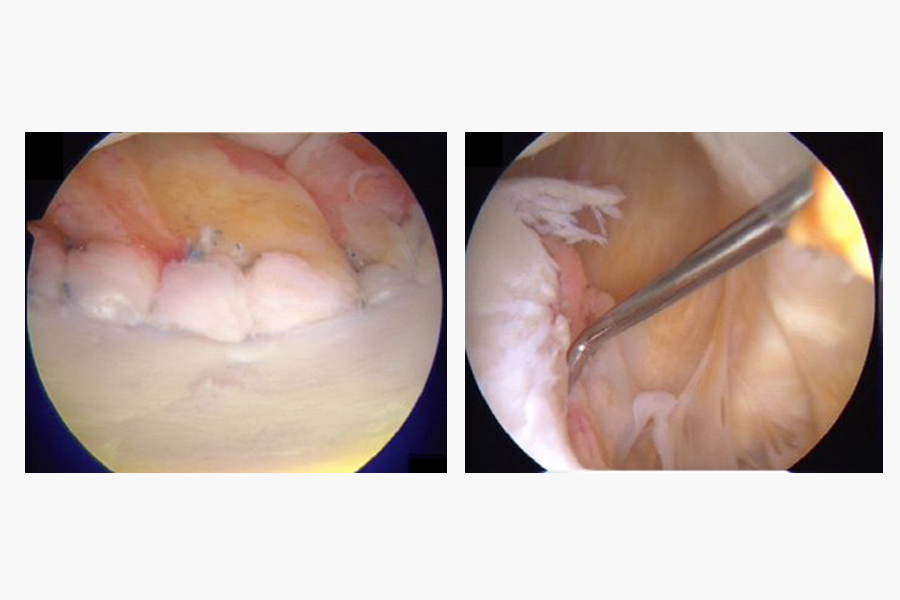
Shoulder Labral Injury
A shoulder labral injury refers to damage or a tear in the labrum of the shoulder joint. The labrum is a piece of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint, helping to stabilize the joint and provide cushioning to the head of the humerus (upper arm bone).
Causes
Labral injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Trauma: A direct blow to the shoulder, a fall, or a sports-related injury can cause a labral tear.
- Overuse: Repetitive overhead motions, such as those seen in throwing sports (e.g., baseball, softball) or certain occupations (e.g., painters, carpenters), can lead to labral injuries over time.
- Degenerative changes: As individuals age, the labrum may naturally become more prone to wear and tear, which can result in labral tears.
- Shoulder dislocation: A severe shoulder dislocation can cause a labral tear, as the labrum is often damaged during the dislocation process.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of a shoulder labral injury include:
- Shoulder pain, especially during certain movements or activities
- A popping or clicking sensation in the shoulder
- Decreased range of motion in the shoulder joint
- A feeling of instability or "looseness" in the shoulder
- Weakness in the affected arm or shoulder
Diagnosis
To diagnose a shoulder labral injury, a healthcare provider may use various methods, including a physical examination, imaging studies (such as MRI or CT scans), and possibly an arthroscopy (a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a tiny camera into the shoulder joint).
Treatment
Treatment for a labral injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's individual circumstances. Common treatment options include:
- Conservative measures: Rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage mild labral injuries.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Surgical repair: In cases of severe or symptomatic labral tears, surgery may be necessary.
- Arthroscopic surgery is often performed to repair the torn labrum.
- Rehabilitation: After surgery, patients typically undergo a rehabilitation program to regain strength and range of motion in the shoulder.
The specific treatment plan will be determined by a healthcare provider based on the individual's condition and needs.
It's important to seek medical attention if you suspect a shoulder labral injury, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve long-term outcomes. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on the most appropriate treatment approach for your situation.