- +91 7012749886
- [email protected]
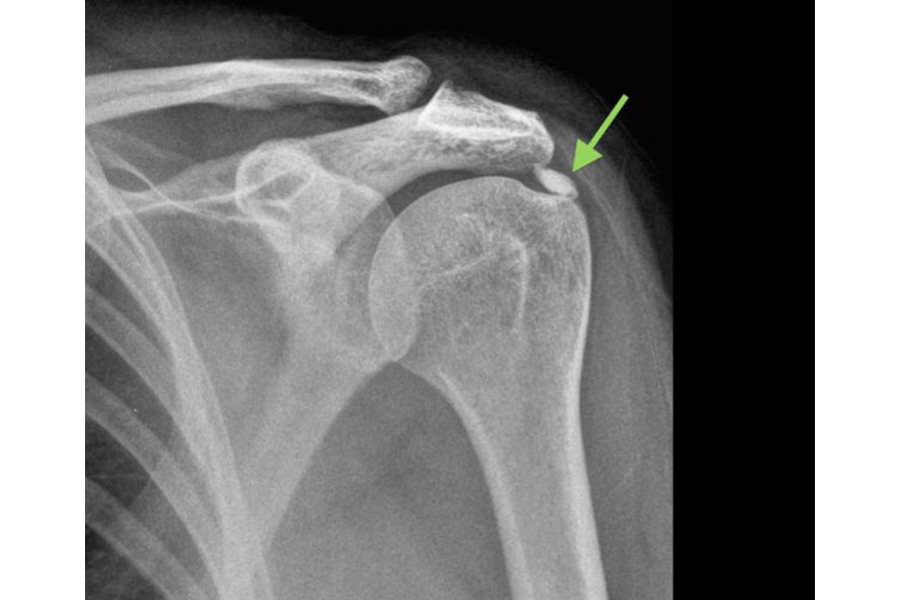
Calcific tendinitis of the shoulder, also known as calcific shoulder tendinopathy or calcific deposit disease, classified as an enthesopathy, is a disease characterized by the deposition of calcium phosphate crystals in the rotator cuff tendons. It is a common orthopedic condition that can cause significant shoulder pain and discomfort. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscle tendons that help stabilize and move the shoulder joint.
The salient features of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder are:
The exact cause of calcific tendinitis is not fully understood. It is believed to be a combination of factors, including age, genetics, and repetitive microtrauma to the shoulder tendons. The deposits are typically made up of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals.
The most common symptom of calcific tendinitis is shoulder pain, which can range from mild to severe. The pain may be constant or intermittent and often worsens with certain movements or activities. In some cases, the pain can be so severe that it affects sleep.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasound, MRI and CT scans. These tests can reveal the presence and location of calcium deposits within the affected tendons.
Treatment options for calcific tendinitis of the shoulder depend on the severity of symptoms, the amount of calcification and associated rotator cuff muscle tendon pathology. These may include:
Recovery from calcific tendinitis of the shoulder can vary depending on the chosen treatment method and the individual's response to it. Some people may experience relief from symptoms within a few weeks of non-surgical treatments, while others may require several months of rehabilitation after surgery.
It's essential to consult us, if you suspect you have calcific tendinitis of the shoulder. We can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific condition and needs. Early intervention can help manage pain and prevent complications associated with this condition.